Bluetooth Low Energy Range: The 6 Parameters That Affect
The reason why Bluetooth Low Energy can achieve uA-level power consumption and can work for half a year or more when powered by a button battery is the special sleep mechanism of Bluetooth Low Energy. A simple summary is to start the radio frequency at a specific time and transmit it quickly. After completing the data, turn off the radio frequency and enter the sleep state, that is to say, during the BLE operation, the radio frequency is in the off state most of the time, so its power consumption can be very low.
Parameters Affecting Bluetooth Low Energy Power Consumption
The parameters that affect power consumption mentioned in this article are based on the Bluetooth Low Energy protocol stack, excluding the power consumption caused by the hardware itself. It contains Advertising Interval, Connection Interval, Slave Latency, Supervision Timeout, Scan Window, Scan Interval.
Advertising Interval
Each time a BLE device broadcasts, it will send the same message on three channels. These messages are called a broadcast event, and the time between two adjacent broadcast events is the advertising interval. The definition of the advertising interval is shown in Figure 1 (the picture is from Core_v5.0, Bluetooth core protocol 5.0)
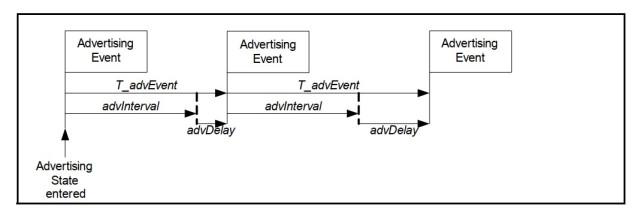
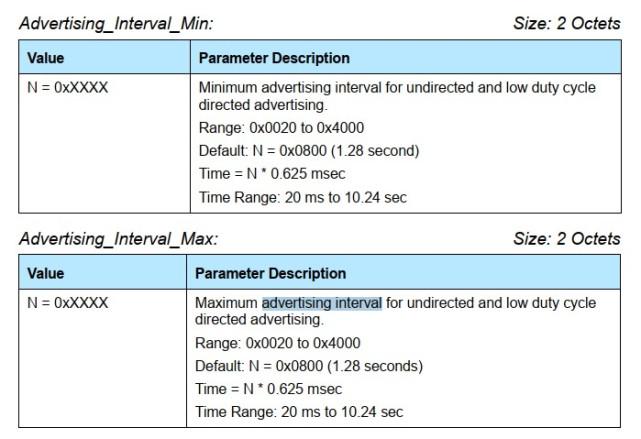
The advertising interval is for the slave device. The advertising interval determines the advertising frequency of the slave device. Do you say that the power consumption of sending data once per second is high, or the power consumption of sending data ten times per second is high? Therefore, the BLE advertising interval is increased, so that the number of broadcasts per unit time is reduced, which can effectively reduce power consumption. The range is shown in Figure 2 (picture from Core_v5.0, Bluetooth core protocol 5.0)
Connection Interval
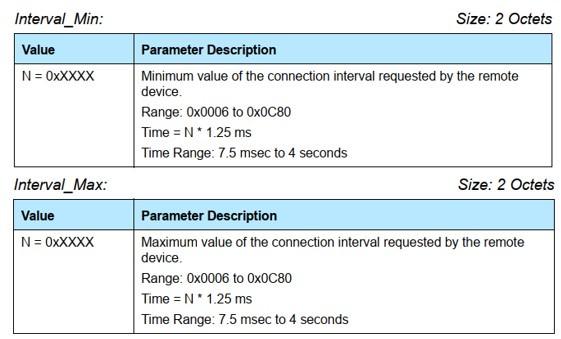
After the BLE host device and the slave device establish a connection, the interval for data interaction is called the connection interval. Note that after the master and slave devices establish a connection. The definition of connection gap is shown in Figure 3 (the picture is from Core_v5.0, Bluetooth core protocol 5.0)
The connection interval refers to the frequency of interaction between the host and slave devices. Increasing the connection interval can effectively reduce power consumption. The parameter range of the connection gap also has a specified value, as shown in Figure 4 (picture from Core_v5.0, Bluetooth core protocol 5.0)
Slave Latency
Slave Latency is the number of BLE connection intervals the slave can sleep in before the connection is terminated. In order to illustrate this concept vividly, reference is made to Figure 5 for explanation.
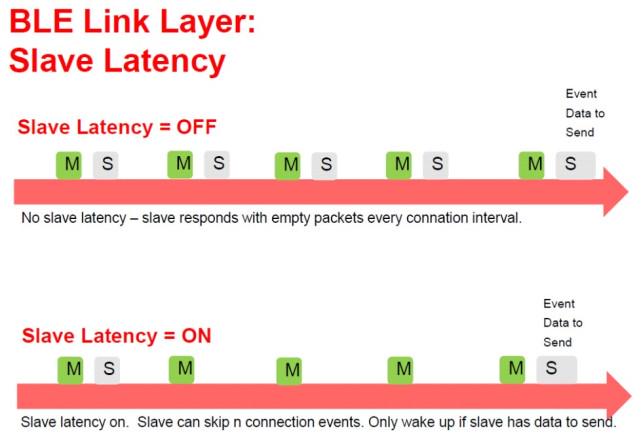
It can be seen from the figure that when the slave device is closed with a delay (that is, when it is equal to 0), every data interaction slave initiated by the host must respond. When the slave device is opened with a delay (when it is equal to 3 in the figure), the slave can ignore 3 data exchange requests initiated by the host and continue to sleep.It can also be seen from Figure 6 that when the slave device is turned on for a delay, the slave device is in sleep for more time, so the device can save more power.
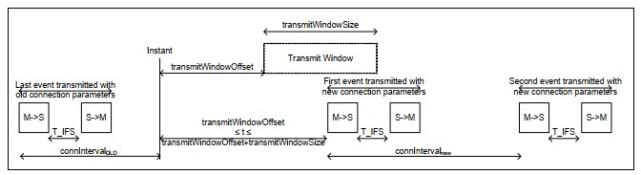
Supervision Timeout
The supervision timeout is also called monitoring timeout, which refers to the link monitoring timeout period of the LE link, which must be an integer multiple of 10ms. must meet: Timeout >(1 + Latency) * Interval_Max * 2。The supervision timeout range is shown in Figure 6 (picture from Core_v5.0, Bluetooth core protocol 5.0)

Scan parameters: Scan Window, Scan Interval
The scan parameters are specific parameters of the Bluetooth host device. Each time the device scans, the device turns on the receiver to listen to the broadcast device, which is called a scan event. There are two scan parameters: scan window and scan interval. As shown in Figure 7 (picture from Core_v5.0, Bluetooth core protocol 5.0)
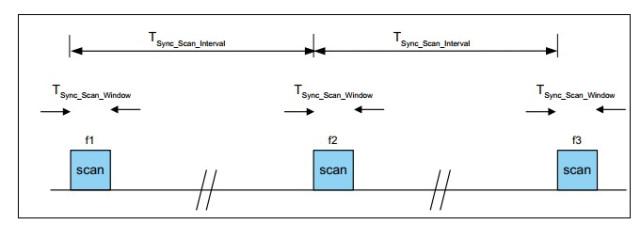

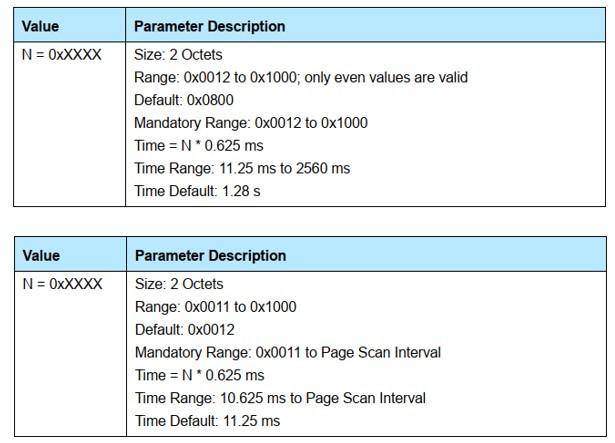
- Scan Window:The scan window refers to the time width of one scan, that is, the scan duration. Shorter duration consumes less energy.
- Scan Interval:The scan gap refers to the interval between the start times of two consecutive scan windows. That is, it can be understood as the scanning frequency, and the lower the frequency, the less energy is consumed.
It should be noted that the scanning window should be smaller than the scanning gap.The parameter range is shown in Figure 8 (picture from Core_v5.0, Bluetooth core protocol 5.0)